At no point in our species’s history has the human race consumed more energy than we do today.
Even with all our machines, factories, and gadgets, the earth’s surface receives more energy from solar radiation in an hour than the billions of us can collectively consume in an entire year.
Simply put, the sun emits a year’s worth of energy in less time than it takes to get a tan at the beach!
Advances in technology allow us to harness the sun’s energy and use it in our day-to-day lives. This is solar power! Let’s take a closer look at solar power and the trends we see now and in the future.
Define Solar Power
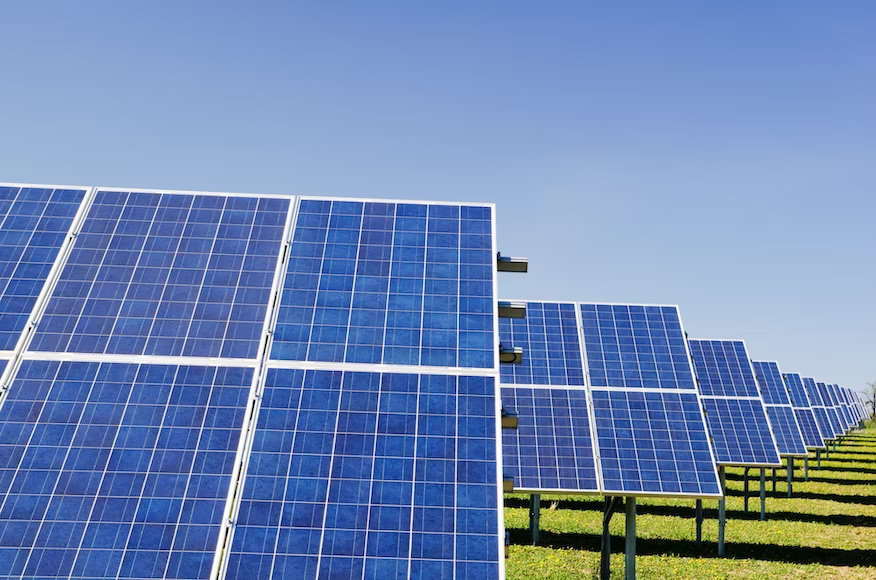

Solar power is energy converted from sunlight into electricity. It can be directly converted through solar panels. Concentrated solar power uses the sun’s heat to generate steam that spins generator turbines.
Solar power can also refer to rudimentary uses that concentrate the sun’s heat into solar ovens, solar water heaters, passive solar heating, and solar cookers.
Check out this TED-Ed video to understand exactly how solar panels work!
In This Article:
- Define Solar Power
- Ways We Harvest Solar Energy
- Growth of Solar Electricity
- How Do Solar Panels Work?
- 5 Types of Solar Installations
- Off-grid Solar Vs. On-grid Solar
- Is Solar Energy Renewable?
- Trends in Solar Technology
- Final Thoughts
Ways We Harvest Solar Energy

There are many ways to harvest and use the solar energy provided by the sun. Let’s take a brief look at each one.
Solar Electricity
Despite some glaring disadvantages of solar energy, this is still the most popular and fastest-growing application of solar technology around the world.
Solar panels can be installed on a residential roof to offset grid power during sunny days. The best renewable energy source for the future may be solar farms in space.
They could provide a large portion of the earth’s electricity needs without taking up terrestrial real estate.
Solar water heaters
Solar energy systems are also used to provide water heating solutions in homes across the country. This technique uses rooftop cells to absorb and transfer the sun’s heat to the water tank.
Many people also use solar water heaters to heat swimming pools. This0+ involves circulating water in a collector heated by sunlight, then pumping it back to the pool.
These are brilliant because they save precious natural resources for more important applications while taking advantage of the sun’s heat that cascades down every day.
Solar lighting
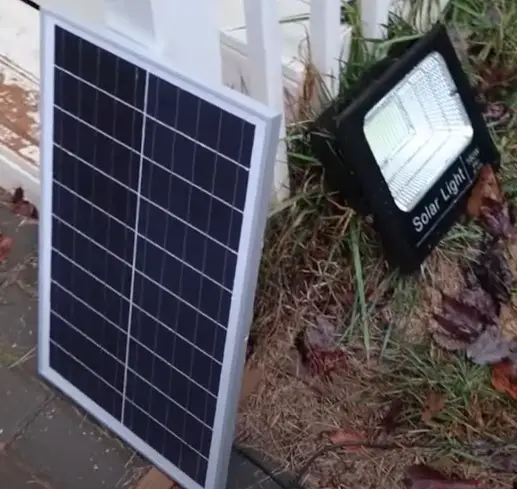

Solar lights are probably the most common and readily available form of solar technology in the country.
They are typically used in home landscaping and road signs and can be found as security lights, street lights, and ambient lanterns, Christmas lights, fairy lights, and torches.
The best outdoor solar lights are relatively inexpensive and will serve you for years to come without using batteries or adding to your electric bill.
Portable solar Chargers
The best solar charger technology has enabled the development of portable and even foldable chargers.
These are incredible because you can take them with you on the go to charge your devices, keep camp lights running, and even power your off-road trailer with the sun’s rays.
There are also watches with in-built solar cells, and it’s the technology needed to integrate PV cells into modern phones already exists.
Solar thermal energy Heaters
Solar thermal heating systems involve capturing the sun’s heat and circulating it into the home. These are typically mounted on the roof and circulate water through to absorb the sun’s heat.
The hot water is then circulated throughout the home, radiating heat to warm the indoor space.
A much older technique is passive solar home design. This is accomplished by carefully selecting building materials and considering the placement of windows to maximize solar heat gain.
If done right, it’s the cheapest and easiest way to heat homes and business spaces since it uses passive solar energy.
Solar ventilation (Transpired Solar Collector)
The trade name of the inventing company is SolarWall.
These are passive preheating systems that help reduce the energy load on central heating systems for homes and businesses during the cold winter months.
The solar wall uses passive solar heating to circulate pre-warmed air toward the fresh air intake of the central heating system. This greatly reduces the amount of energy needed to warm the building.
Solar Air Conditioners
These are small units that use a solar panel to power the air conditioner’s condenser.
It works like a regular air conditioner, but the power is generated by an attached solar panel or panel array.
There are small personal-sized air conditioners with a single panel and large units that can cool a large room with an array that is mounted outdoors.
Solar transportation
By solar transportation, we’re referring to all the ways that humans are attempting to power vehicles using the sun.
This includes experimental solar cars that run only via attached solar panels and new solar EV charging stations.
We’re in the middle of an EV revolution, but more people are realizing that they aren’t saving the planet by driving an electric vehicle that’s powered by a fossil fuel charging station.
So solar charging stations are increasing in number so that transportation can be truly converted to green energy.
Solar charging stations also enable EV chargers to be placed in areas where there is no electric infrastructure.
Growth of Solar Electricity

The solar industry has experienced rapid growth over the past decade, making solar energy the fastest-growing electricity source in the United States.
It is expected to account for half of all renewable energy generation in the US by 2050.
Just how fast is solar power growing? It took the industry 40 years to complete its one-millionth installation.
Just three years later, in 2019, the Solar Energy Industry Association (SEIA) announced that the US has over 2 million solar installations.
That number will grow to 4 million in 2023. In 2024, experts predict that there will be one solar installation per minute, up from one installation every 10 minutes in 2010.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
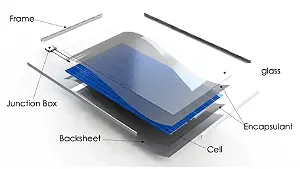
Solar panels convert light from the sun into electricity. They consist of photovoltaic cells, each of which is contained within a larger silicon cell.
The silicon cell is in turn encased in glass and metal to protect it from the elements.
The photovoltaic cell is the most crucial component of a solar panel. How does it work?
- A PV cell is made of semiconductor material, usually silicon, that absorbs photons emitted by the sun.
- These tiny packets of energy carry solar radiation, and once they strike the semiconductor material, they release electrons from the silicon atoms.
- The surface of the PV cell is usually coated with anti-reflective material to minimize photon loss during reflection.
- The silicon layer on top is doped with phosphorus atoms (has one more electron than silicon), and the other layer is doped with boron atoms (has one less electron than silicon).
- As a result, the cell creates an electric field when the electrons are excited by light photons, pulling those displaced electrons into a directional current.
- Wires then feed the direct current (DC) to a solar inverter which converts it to alternating current (AC), which is what you need to turn on and run your home appliances.
Normally, inverters are placed as close as possible to the solar panels. However, they usually make some noise when generating electricity, so they’re sometimes put in the garage or shed.
From here, the AC flows to your distribution panel to power all the electrical devices in your home.
5 Types of Solar Installations

Most solar panel installations use the same technology but differ in purpose, size, location, and price.
Installations are generally categorized into four groups; residential, commercial, community solar, and utility solar.
Residential solar
Most residential solar systems are rooftop installations, although it’s possible to have ground installations.
Also, most of them send their electricity directly to your home and transfer any excess to the grid. This offsets your electricity bill in a process called net metering.
Commercial and Industrial Solar
These are the solar energy systems installed in any business, regardless of size. You can see such installations on rooftops in small businesses, parking lot canopies, and wide-open fields.
Factories that go solar have to purchase large tracts of land to cover with solar panels. Solar can power any size of industrial factory, but the land requirements are massive.
Utility-scale solar
Today, power plants are increasingly incorporating large-scale establishments of renewable energy resources like solar energy to provide electricity.
Utility-scale solar installations can get massive, ranging anywhere from 500 to 30,000 times the size of residential solar installations.
Community solar
How does community solar work?
These are large-scale solar farms designed to make solar power accessible to people and sometimes businesses that can’t install solar panels on their premises.
The farm is usually situated in an open area around the neighborhood where the solar energy is directed.
It can also be powered by a network of individuals who pool their home solar electricity generation into the community solar project.
Off-grid Solar Vs. On-grid Solar
Many homeowners often wonder whether their solar installations can allow them to go completely off-grid. After all, the more disconnected you are from the grid, the lower your monthly power bill.
Off-grid solar
Off-grid generally means you get all your power from your home’s solar system, even at night and during bad weather. For this to happen, you need to connect a solar battery bank to your home.
That way, surplus energy generated during the day is stored in the battery bank for use at night. Since you don’t rely on the grid for electricity, you don’t have to pay electricity bills.
While this sounds great, it’s not as easy as it sounds.
First, you have to find a reliable battery bank with enough capacity to cater to your daily energy needs, plus any surplus demands.
Even then, some city zoning laws have restrictions that prevent homes from going completely off-grid. So, you’ll still be paying that bill, even with batteries installed.
This is not the case everywhere, but you’ll definitely want to check into your local and state laws before making that investment.
On-grid Solar
On-grid solar is probably what you already have or will have when you decide to install solar energy equipment.
Such systems are designed to supplement the home’s electricity demand.
They don’t necessarily require a battery bank as surplus electricity is sent to the grid, allowing you to enjoy the cost-saving benefits of net metering.
If you use a battery bank, the generated electricity first fills the battery before sending any excess electricity to the grid for net metering.
Is Solar Energy Renewable?
Perhaps the biggest appeal to solar energy lies in the fact that the sun is the ultimate renewable resource.
However, there are some major cons of solar panels we have to cover in this topic.
While the sun may shine for billions of years, our supply of the rare metals we use to build solar panels could run out within this generation.
So, from this perspective solar energy is definitely not renewable. The key will lie with those who are currently developing safe and renewable alternatives to components like lead, silica, cadmium, and indium.
When the problem of solar panel waste pollution and natural resource depletion is solved, solar will really bloom into green energy for the future.
Trends in Solar Technology

Solar technology is getting better with time, and there are some big solar technologies we may see in the coming decade.
Floating Solar Farms
Floating solar farms (floatovoltaics) are solar stations constructed on the water instead of on land.
They’re an innovative solution that will allow countries with limited open spaces to construct farms of enormous magnitude if done right.
Using floatovoltaics also carries a couple of benefits.
- There’s no money spent on buying land. This reduces the opportunity cost of establishing solar farms on real estate and lowers the total energy cost.
- The water also helps cool the solar panels, reducing fluctuations in the PV cells’ efficiency.
This concept has been around for a while. The world’s first floatovoltaic system was installed in California in 2008.
Today, there are over 100 such installations globally, seven of which are in the U.S. and around 80 in Japan.
As this technology becomes more mainstream, don’t be surprised if you see a floating solar farm on a lake near you.
Integrated Photovoltaics
Solar panels are typically placed on the rooftops of buildings, which often have limited space. Therefore, researchers are developing building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) to use the vertical space of skyscrapers.
Also known as quantum dot solar cells, this technology has the potential to be used on windows without blocking natural light from passing through the glass.
We may also see an extension of BIPV technology on solar skins – cheap and efficient paper-thin panels applicable to almost any surface.
Harvesting Solar Power at Night
Unavailability at night is probably solar’s biggest disadvantage.
Fortunately, some people believe that this can change. Researchers from the University of California are developing new solar technology that can generate power 24/7.
How will it work?
Solar energy received by the earth during the day escapes as solar radiation at night. This new technology will capture that nocturnal solar radiation and convert it into electricity.
Perovskite Crystal
There may be a chance that we’ve reached the peak efficiency of silicon PV cells.
Therefore, scientists are working on perovskites as the next evolution of solar panels.
Currently, they’re being used to enhance the efficiency of silicon cells so panels can convert more solar energy into electricity.
However, if the technology advances well enough, there is potential for perovskites to be used independently in PV cells for maximum solar conversion efficiency.
Final Thoughts
It’s quite clear that the benefits of solar energy far outweigh the disadvantages.
The long-term cost-saving benefits also beat the up-front costs of purchasing and installing solar panels.
The manufacturing process is very pollutive to the environment but solar is still far less of a pollutant than burning and mining fossil fuels.
This is the most important aspect of solar energy and why so many people in the world are eager to adopt the resource.
What are your thoughts on solar energy? What’s the new technology that you’re most excited about? Let us know in the comments below!
